Semantic Search Using Word Mover Distance
Introduction
We all use ctrl + f extensively in our works to search for a string in a web-page or text document. This search is done at a lexical level i.e. the search matches the string strictly at character level. If our search query is slightly mis-typed it might not retrieve any matches. More interestingly, we might vaguely know what we want to search for but can’t exactly remember the exact keyword. In such cases, semantic search would be extremely useful. This blog will discuss such an example wherein one wants to search for text related to but not exactly containing a particular keyword or set of keywords. We use word mover distance to “search” these semantic-search results.
A word on dataset
We use the Constitution of India document for this task.
This dataset consists of the full text of the constitution. And we use this document as an example to demonstrate how the semantic search tool could be useful in certain scenarios. One fundamental characteristic of this document which helps on the demo is that it is structured by articles, hence we use the article numbers as ids for each chunk of text. Upon entering the search query, the engine outputs top k relevant such chunks.
Data pre-processing
-
We use beautifulsoup to iteratively scrape the structured text data from this web url article by article.
-
Next, we use TextBlob to retain only the noun phrases in the texts. This is an aggressive version of getting rid of stop words and inconsequential words moreover.
-
Finally, using WordNetLemmatizer from nltk toolkit, we lemmatize the retained noun phrases from each article text from the Constitution of India text
Details of data pre-processing can be found in this notebook.
Word Mover Distance:
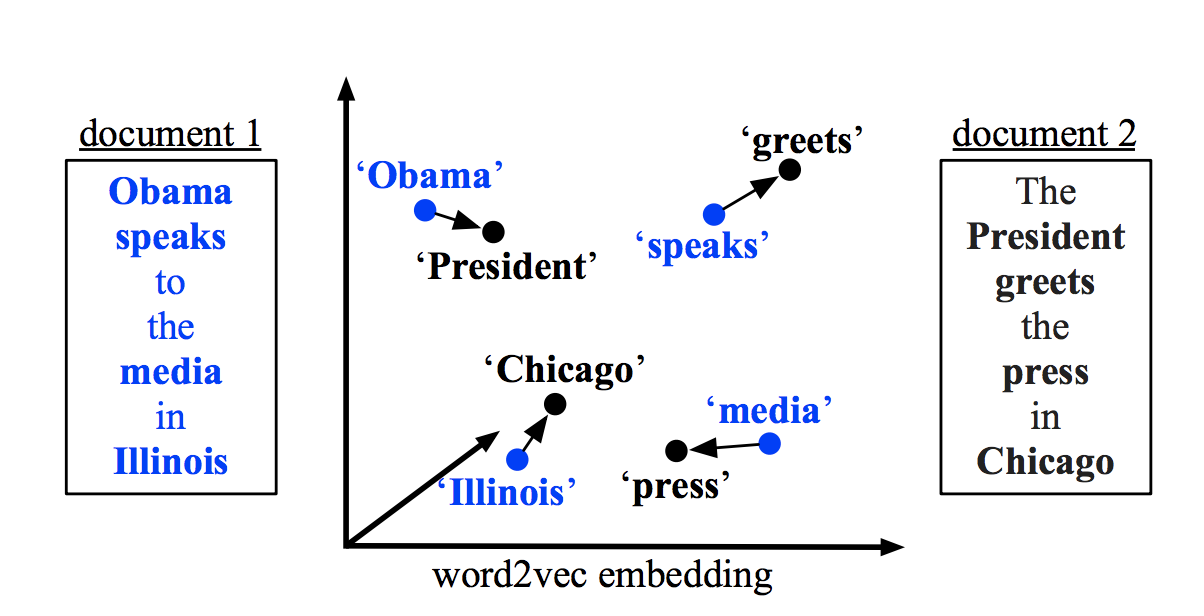
Word mover distance is in simple words a measure of smeantic distance between two documents or collection of words. WMD uses word embeddings to calculate the distance so that it can calculate even though there is no common word. The assumption is that similar words should have similar vectors.
Word2vec embedding for each word from document a is compared with word2vec embedding for each word in document b. At the end the algorithm will choose the minimum transportation cost to transport every word from sentence 1 to sentence 2. Details can be found in the original paper. I also found this article light and helpful.
Code
The search dashboard implemetation alongwith related research notebooks can be found here. Dashboard was created using plotly dash and research was done using gensim’s wmd using glove word2vec, nltk’s wordnetlemmatizer, textblob’s nounphrase extractor, and beautifulsoup based scraper.
Sample Results
Here are some interesting success and failure cases of this search engine where a regular lexical search is not sufficient and a semantic search is needed instead.
- bhasha (language, in Hindi) - this word, though not mentioned anywhere in the text itself, is clearly referring to language. Surprisingly the engine gets it right, thanks to the global generalisability of the glove word vectors.

- free speech - this is a popularly used phrase in Indian politics and society at large. Again, although not presnt in the text as-is, the engine is able to get the relevant articles as the 4th and 5th matches; the first three matches are clearly failures of the search engine.

- casteism - Surprisingly the results of this query gets the most relevant articles and the best part is that none of those articles even have the word “caste” in them, let alone “casteism”.

- child labour - This is a failure case, where the engine fails to fetch any decent results.

To add to the failure, if we by mistake type labour as labout, the results start looking better.

Feel free to check out more cases yourself in the dashboard.
Semantic Search Dashboard
Working dashboard is available here
Next Steps
Taking inspiration from this tool, the semantic search functionality can be embedded as a browser plugin, where from one can directly look for semantically relevant texts on a web page.
Thank you for reading this post. Hope it was helpful !
