Lessons from writing a deep learning book
After co-authoring a book on supervised machine learning, I was interested in going deeper into deep learning, which has been my area of work and interest for the past few years. Last year, as extraordinary as the year was, I started writing a deep learning book. As the book is out in January, 2021, this post is to share my journey and experience of writing it, as well a sneak peek of what is in the book.

Mastering PyTorch
You read it right, the book is titled - Mastering PyTorch. So, let me first address why the title isn’t Mastering Deep Learning. First, there already are quite a couple of golden deep learning books out there - the one writen by Ian Goodfellow et al. for instance. It did not appeal to me to reinvent the wheel. Second, there are much fewer hands-on resources, especially books, when it comes to deep learning. I personally find hands-on learning to be more effective for someone who wants to build a career in deep learning / machine learning. And therefore, I wrote this book with an applied / hands-on theme to it.
And for doing so, I had to use some deep learning library as a substrate to build up the
knowledge base on. And therein comes the second question. Why isn’t it Mastering TensorFlow ? Although I am not significantly leaning towards one library
compared to another, this decision was a result of 1 - the recent trends indicating rising popularity and coverage of PyTorch as well as,
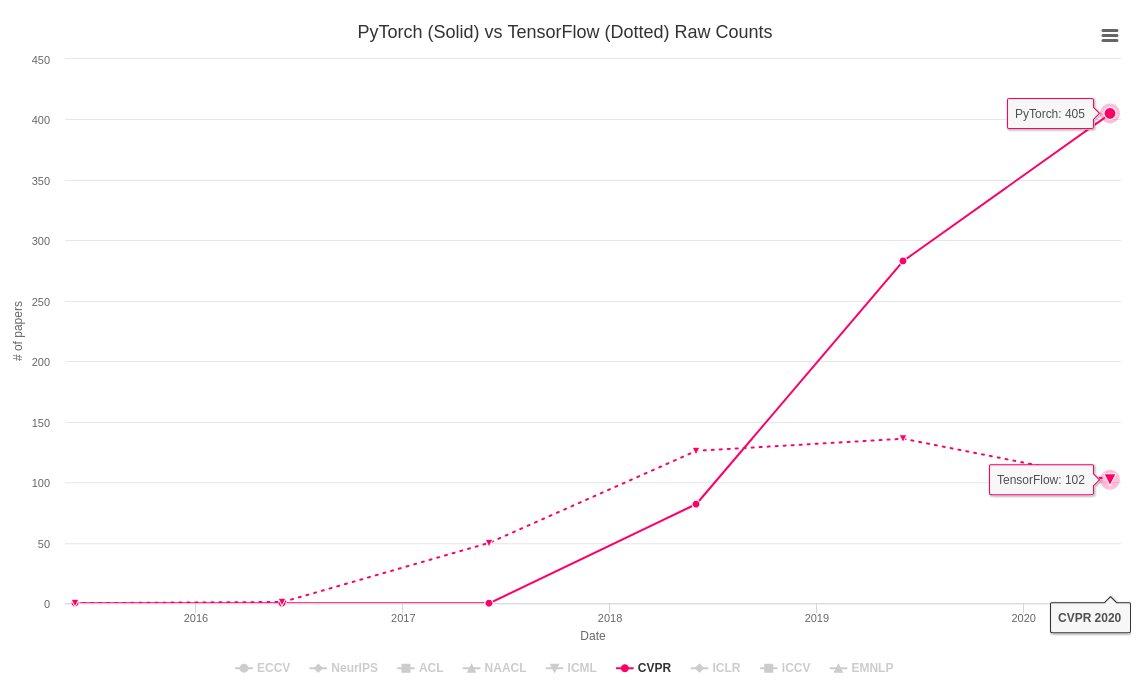
2 - a product preference expressed by the publisher (Packt).
This book hence walks you through different facets of working on deep learning ranging from researching on vision, text and other complex models, to deploying models in production environments, to developing fancy artistic generative AI models, and more, by using PyTorch as the toolkit of development. With this book, you will both get a hands-on deep learning experience as well as learn PyTorch as a deep learning framework, in some depth.
Why another PyTorch book ?
There are already a few good resources for learning PyTorch such as the Deep Learning with PyTorch book or the PyTorch website itself. However, there isn’t a single resource that provides a decent coverage of various deep learning topics that can be explored using PyTorch. More often than not, we end up spending endless hours scanning the PyTorch forum to get PyTorch to work on our area of deep learning, if the traditional resources do not cover it properly. Furthermore, there are tons of blog posts written on PyTorch topics that are not clearly explained in the original resource, and it can be hard to find the good ones as they are all scattered across different mediums. For instance, the documentation around distributed training with PyTorch is not easy to follow and hence there are blog posts like this - https://leimao.github.io/blog/PyTorch-Distributed-Training/ to help us understand.
This book, therefore, is an attempt to provide a holistic resource with a coherent learning experience starting with reviewing the basics of deep learning in chapter 1, to developing a DQN model in chapter 9, to interpreting model predictions in chapter 13. With each chapter containing at least one exercise, the book ensures that all concepts covered across chapters are thoroughly tested in those hands-on exercises, in the form of jupyter notebooks. Besides extensively discussing the fundamentals of the PyTorch library, this book will also enrich your knowledge of the PyTorch ecosystem which is growing rapidly and advancing the pace of deep learning developments.
The journey
I began working on this book in May, 2020 with Packt. As this is a first edition, I decided together with the publisher the contents to place within the book. With the initial 2-line summaries of each chapter in place, I started writing chapter drafts. I used Google Docs as my writing tool. For writing the chapters, I always did some initial research on the contents to be put in for that chapter. Different chapters demanded different volumes of time. I remember spending quite some time on reading up for Chapter 9, which was all about Deep Reinforcement Learning and I wanted to give a broad overview of the field to the readers besides training a DRL agent using PyTorch. Each chapter has at least one exercise - which means that I would design the exercises and push them on the book’s github repository, most of the time even before writing much of the chapter text. Besides the code, the images or figures were another important element to be taken care of. I mostly used draw.io to generate the model architectures, or other schematic diagrams.
Each chapter went through rounds of reviews starting from the basic language review, to technical review, all the way to higher level editorial review. These reviews really helped refine the quality of the content and I am thankful to the Packt team to this end. The book also contains a foreword by my teacher - Dr Gopinath Pillai who currently heads the Electrical Engineering Department at IIT Roorkee. I am also thankful to him for his kind words.
The experience
Writing a book is not easy. My previous writing venture was for a second edition of a book, together with another author. This time, it was just me writing a first edition - and this is truly a different ball game. It was quite intense. Each chapter had a deadline attached to it, which was good for avoiding procrastination but would occasionally be overwhelming especially because I was writing it besides a full-time job.
A key learning for me has been that this whole process has forced me to learn the topic in greater details. One really needs to go several extra miles than the basic understanding of a topic in order to be able to explain it to others. One needs to make sure that all the codes across all the chapters work and with reproducibility; one needs to pay attention to the minuscule details while illustrating a concept using a diagram, and so on. Besides my own learning, I also felt a genuine satisfaction of giving it back, merely because I have been in that situation where I wished I knew of a resource on a topic that could gradually speed me up on that topic.
Finally, I have also gained a rich experience of technical writing along this journey. I am better able to decide what should be covered in the content, how it should be conveyed, why is it important, what should be the order of topics to make the reading coherent, how do we intertwine illustrations / diagrams / codes / exercises within the text, and so on. Furthermore, I have gained a decent understanding of the publishing lifecycle - the different steps involved, from inception, all the way to an Amazon book link.
What you’ll learn ?
Following are the chapters in the book, briefly mentioning the contents within them:
1 - Overview of Deep Learning using PyTorch
-
This chapter revisits the fundamentals of deep learning - neurons, layers, activation functions, optimization schedules, and so on.

Types Of Deep Learning Models -
This chapter simultaneously also recaps the basics of PyTorch - tensor, torch modules, torch functions, etc.
2 - Combining CNNs and LSTMs
- You will learn to build an image caption generator which is a combination of CNN and LSTM models.
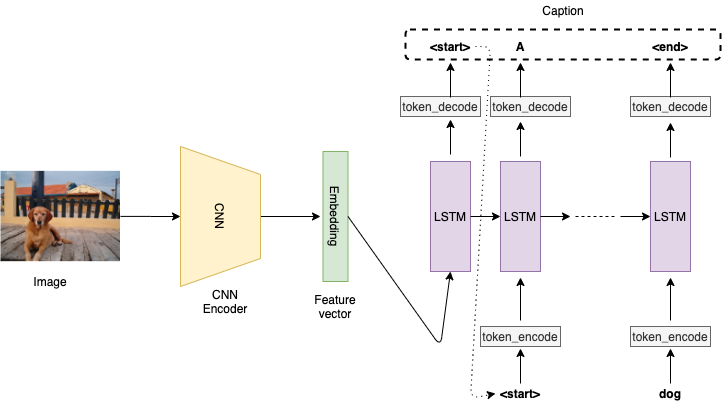
- This chapter is meant to build the momentum to gear up for the next chapters which extensively cover various neural architectures.
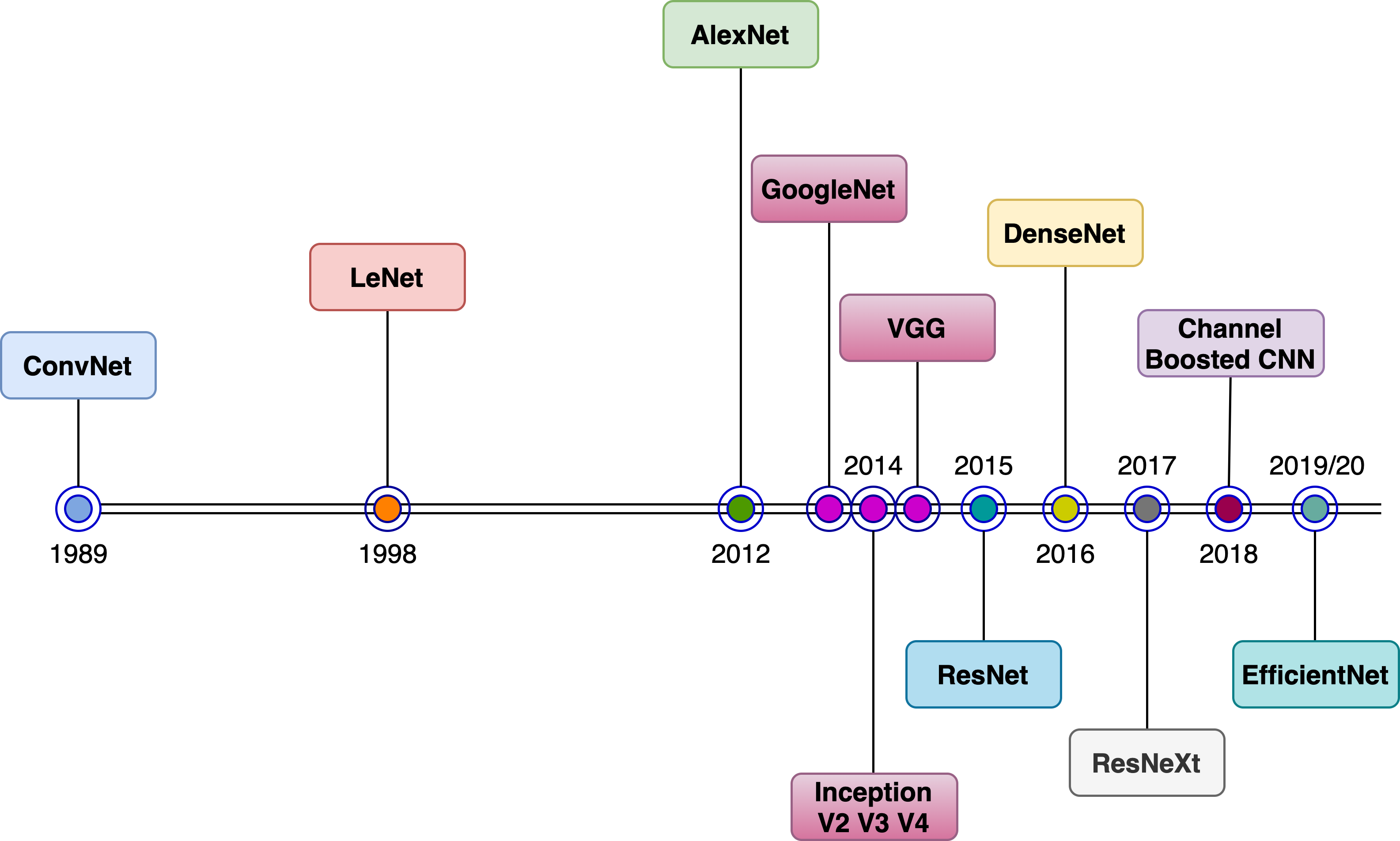
3 - Deep CNN Architectures
- Being one of the biggest chapters of the book, it covers a vast range of CNN model architectures ever since they were invented - starting from LeNet all the way to EfficientNets, with a focus on image classification for the exercises.
4 - Deep Recurrent Model Architectures
- Similar to the previous chapter, this one walks through the evolution of recurrent architectures, starting from vanilla RNNs, to LSTMs, GRUs and beyond.
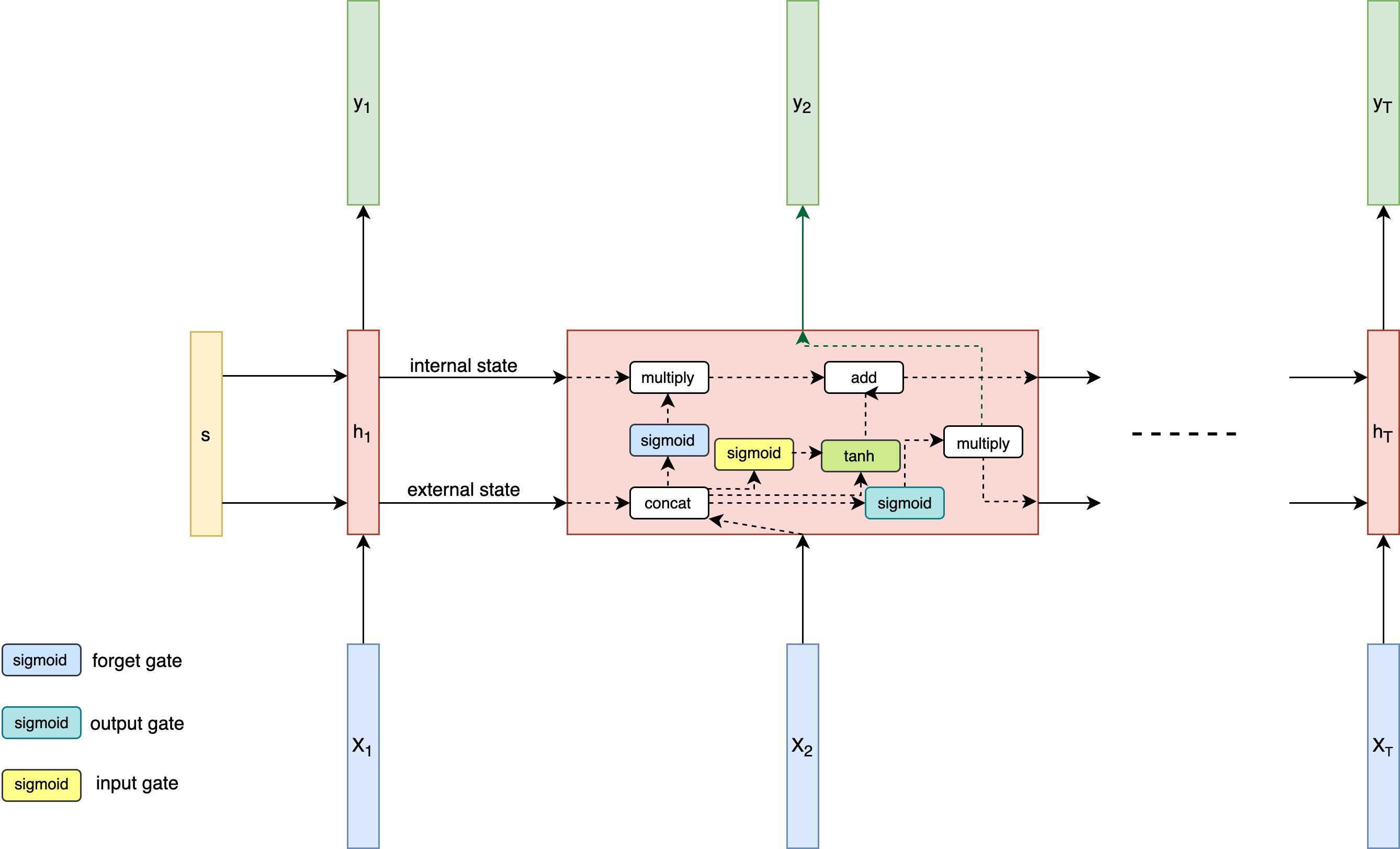
- You will also learn to train sentiment detection RNN and LSTM models using PyTorch along the way.
5 - Hybrid Advanced Models
- This chapter is a conclusion to the discussion of model architectures. It picks up from where we end in chapter 3 and chapter 4.
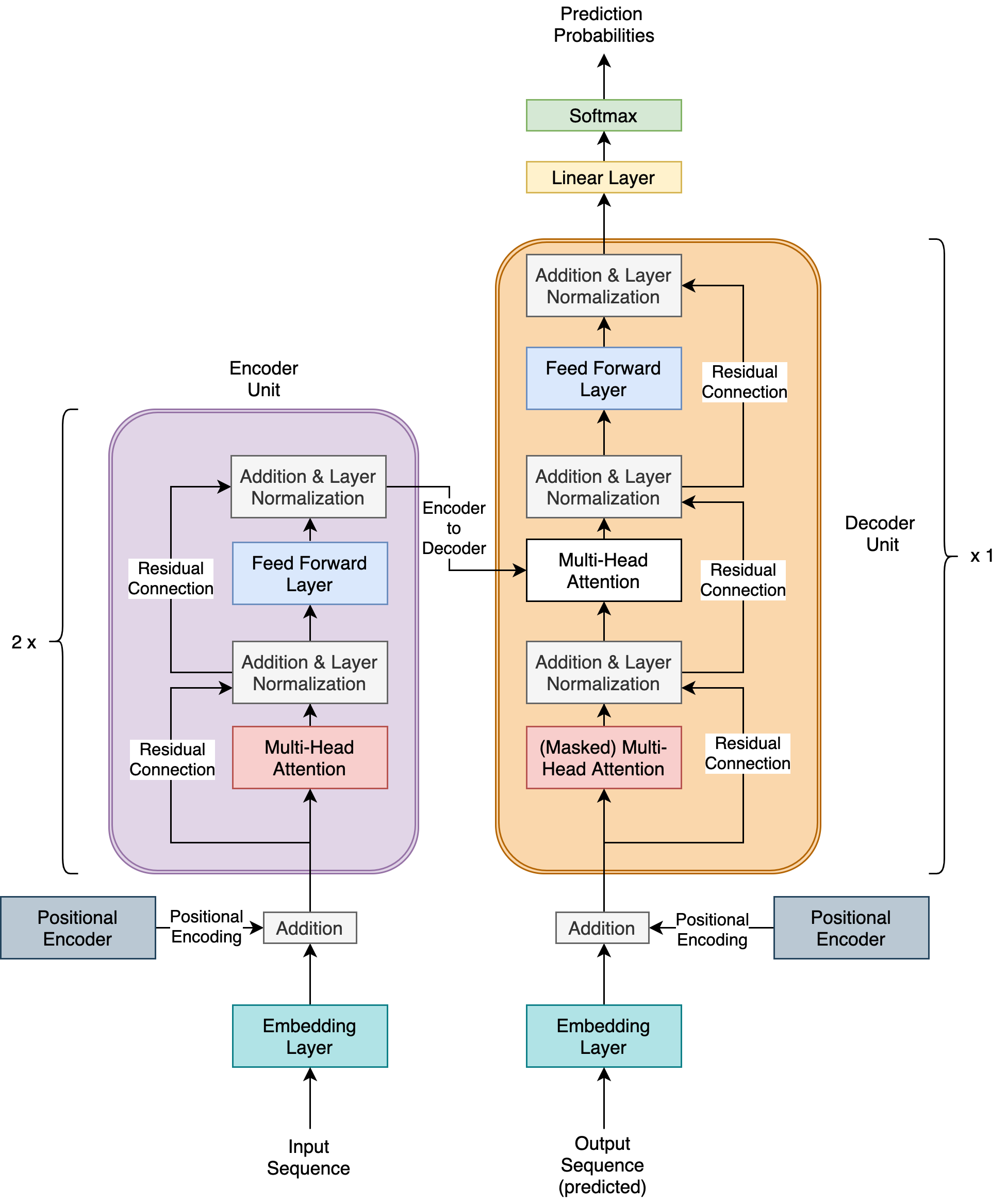
- Continuing from chapter 4, we discuss transformers which have essentially rendered recurrent neural networks redundant. And resuming from the neural architecture search (NAS) discussions at the end of chapter 4, we discuss RandWireNNs which is a well known NAS approach.
6 - Music and Text Generation with PyTorch
- We enter into the exploration of generative artistic AI models in this chapter. First, we use the transformer model discussed in the previous chapter to generate meaningful text. We discuss text generation strategies such as greedy search, beam search, etc.
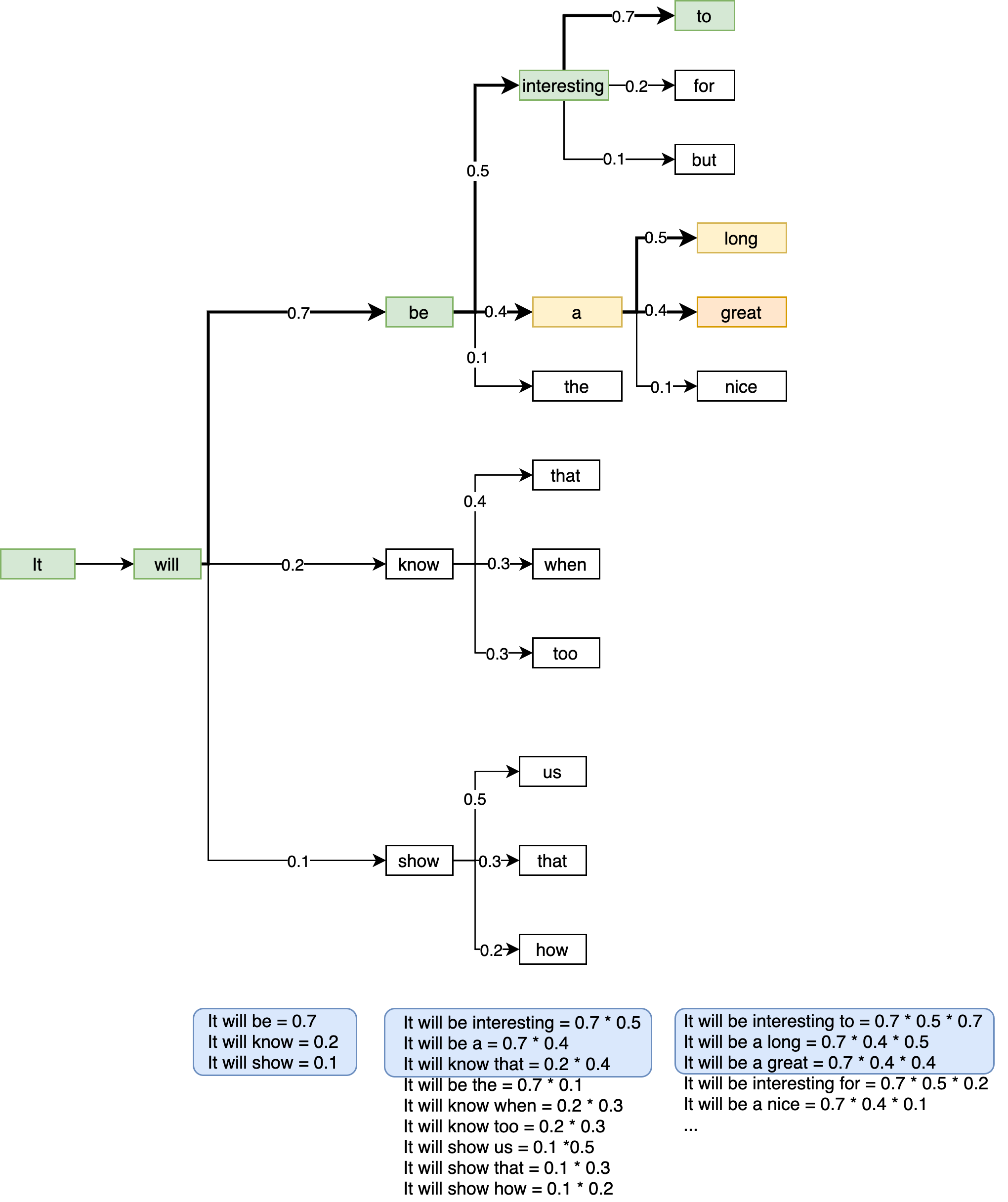
- In the second half of the chapter, we train an AI music composer that should learn to generate Mozart-like compositions. Here is an audio sample generated in the chapter exercise: Generated Clip
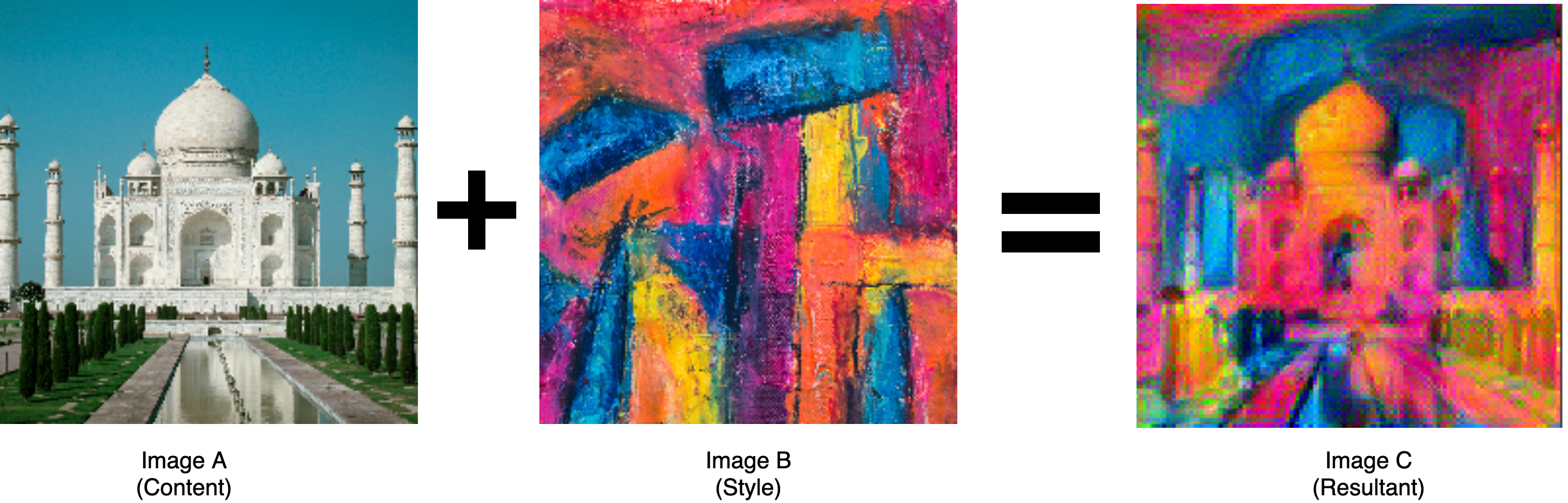
7 - Neural Style Transfer
- Continuing the artistic AI theme from the previous chapter, you will learn to train an NST model which can combine the style of one image with the content of another.

8 - Deep Convolutional GANs
- Concluding the generative models discussion, you will learn to build a DCGAN model in PyTorch on the MNIST dataset.
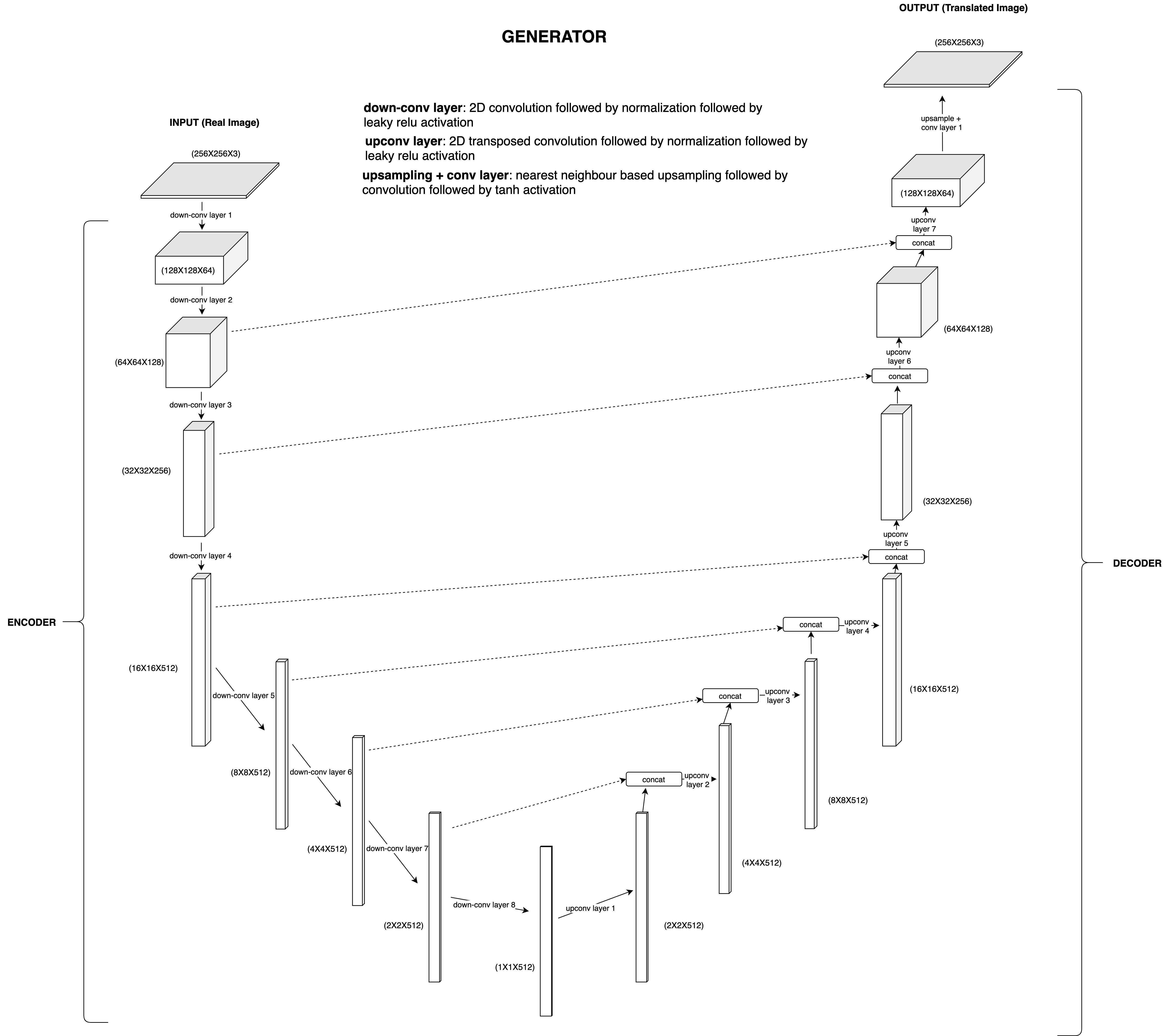
- As a bonus, you will also learn about the Pix2Pix model which is another well-known GAN model that automates image-to-image translations.
9 - Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
This chapter is both a very brief overview of the field of RL, as well as a deep dive into the world of Deep Q-learning Networks (DQNs).
Pong Video Game -
You’ll learn to train an AI video game player for the pong video game using PyTorch and gym.
10 - Operationalizing PyTorch Models into Production
- In this longest and my favorite chapter, you will learn all about serving PyTorch models in production systems using Flask, Docker, as well as using TorchServe. You will learn about the various ways of using JIT-ed PyTorch models via TorchScript.
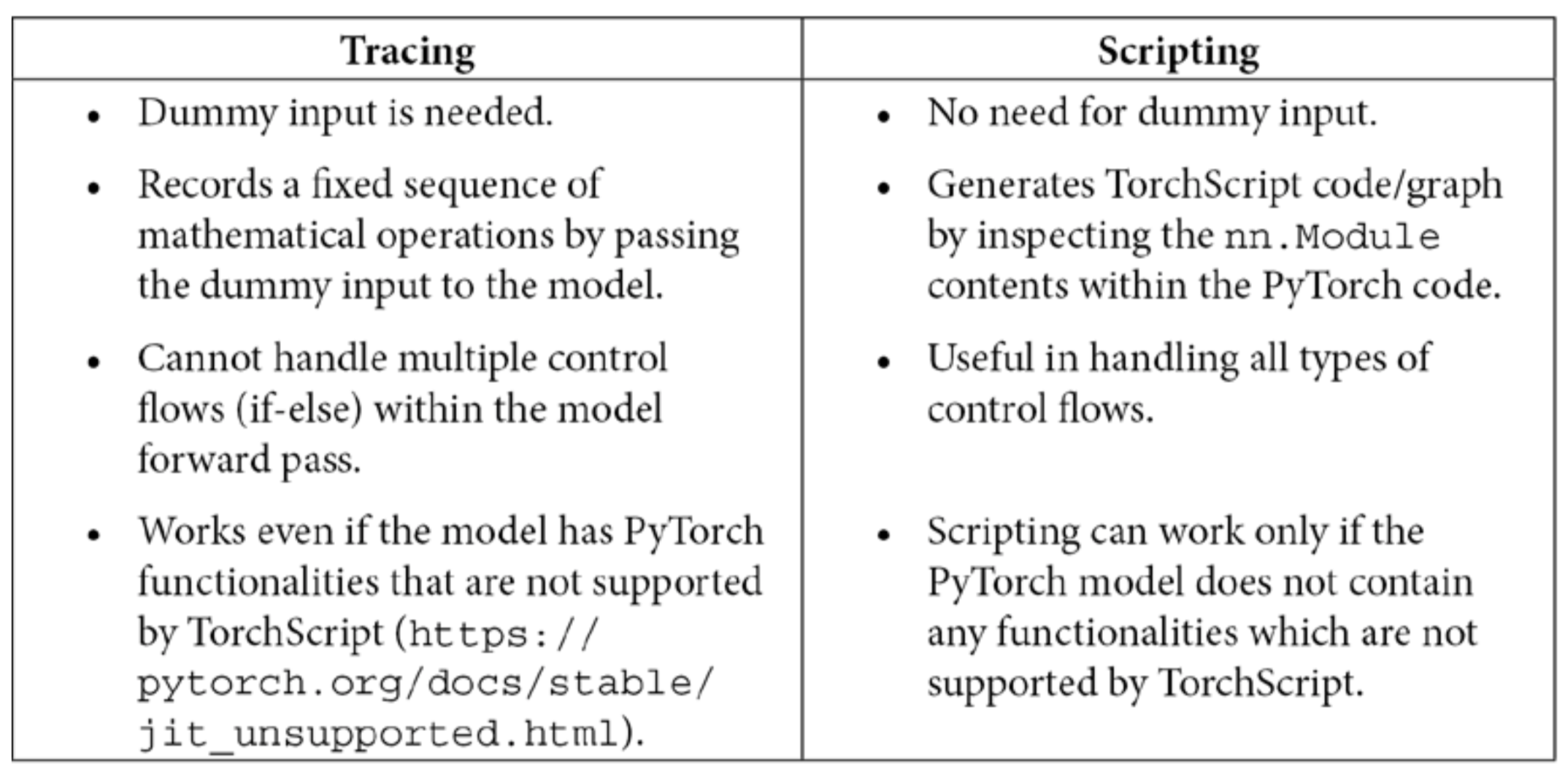
- You will learn how to port PyTorch model into a C++ application as well as using PyTorch model in Tensorflow via the ONNX export format. Finally, this chapter walks through the various ways of working with PyTorch on some of the most common cloud computing platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud and Azure.
11 - Distributed Training
- This chapter focuses on demonstrating how to leverage performance gains in terms of model training time, with the help
of distributed deep learning model training in PyTorch.
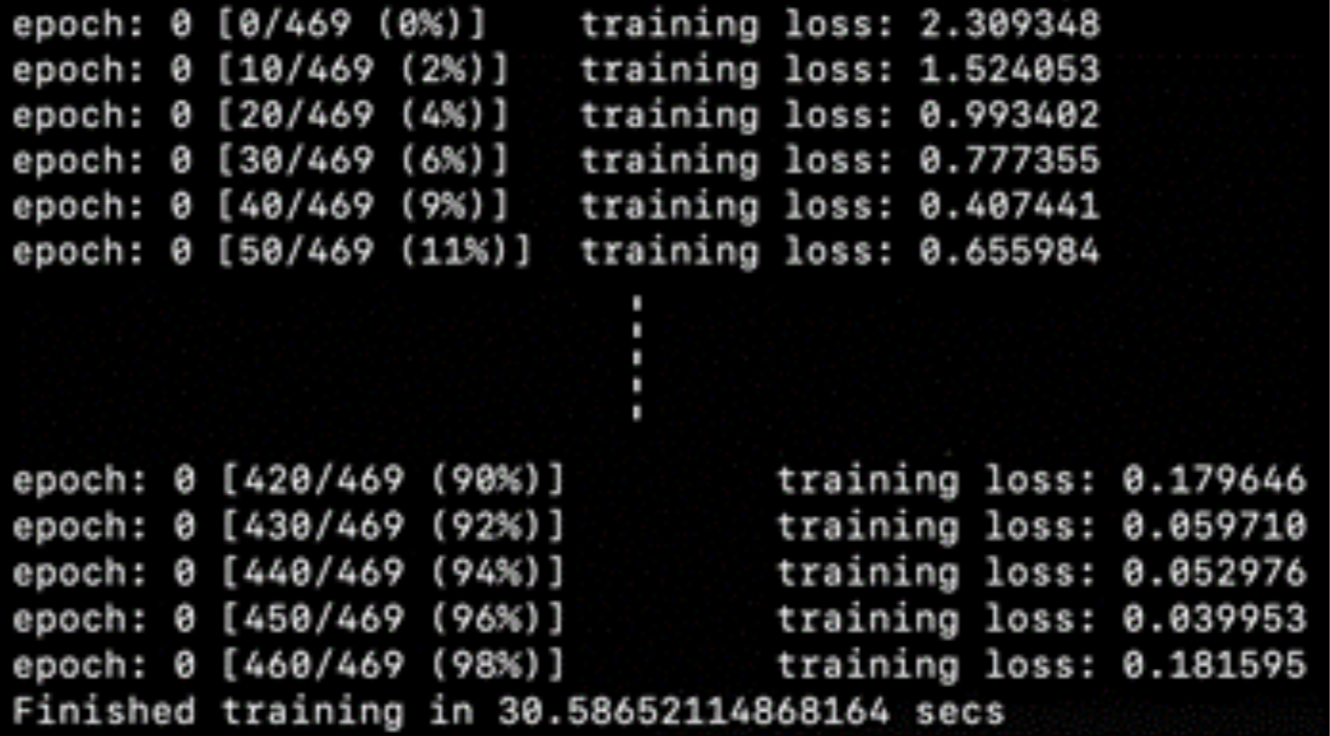
Distributed training logs
12 - PyTorch and AutoML
- The NAS discussions from chapters 3 and 5 aside, this chapter is a deep dive into the field of AutoML which covers both NAS as well as hyperparameter search.
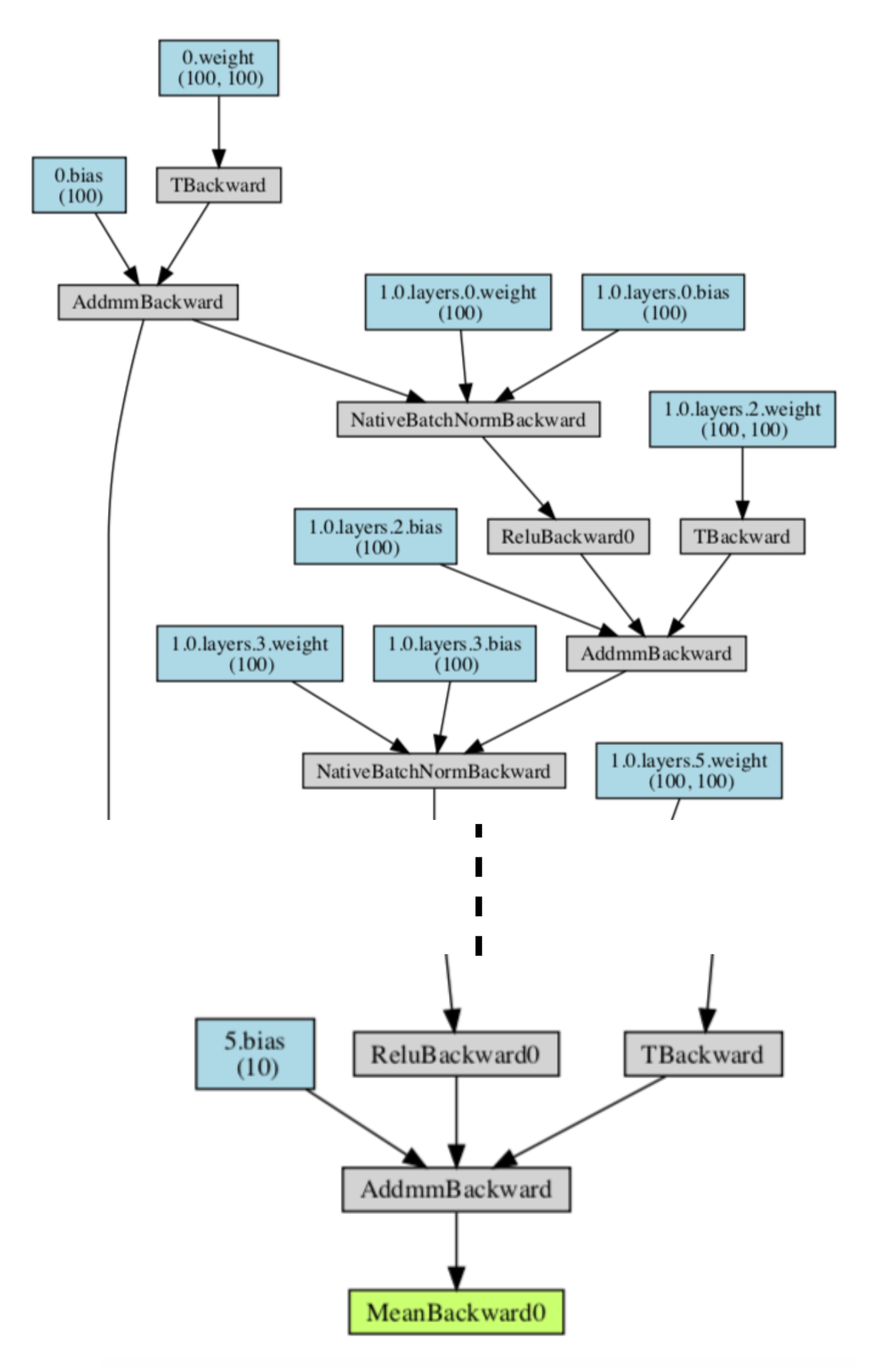
- You will learn how to use AutoPyTorch to perform AutoML with PyTorch as well as Optuna, which is a cool hyperparameter search library for PyTorch.
13 - PyTorch and Explainable AI
- In this chapter, you will learn to reason the model predictions to some extent, by dissecting a trained PyTorch model.
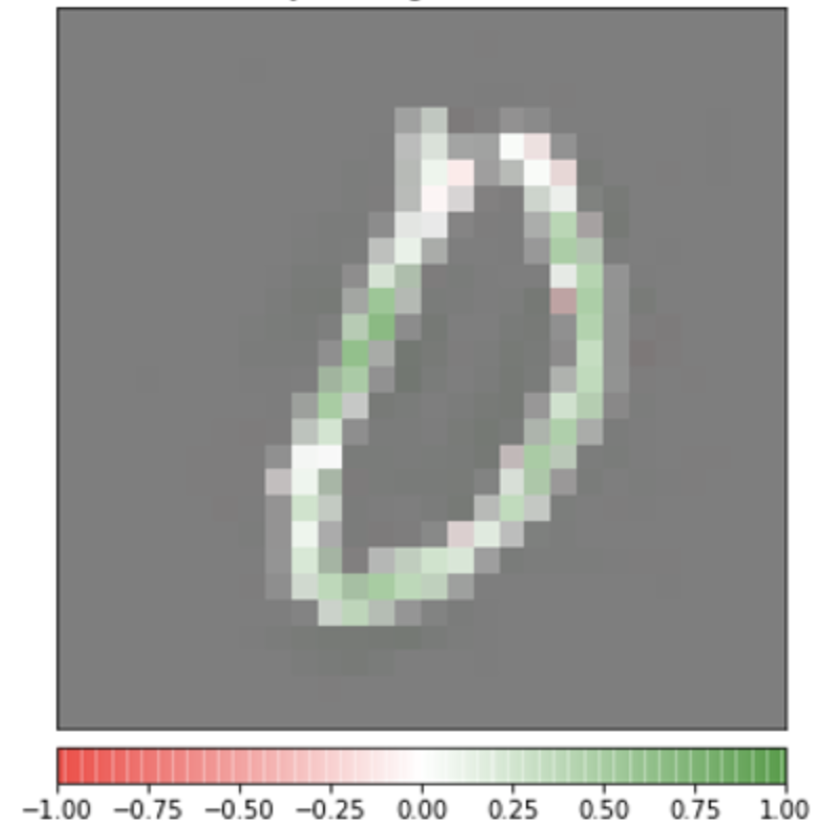
Overlaid Integrated Gradients - This chapter also explores a fantastic model interpretability library called Captum, which further helps investigate the inner workings of a trained model.
14 - Rapid Prototyping with PyTorch
- The final chapter of this book discusses two libraries - fast.ai and
PyTorch Lightning - both of which are aimed at
making the process of training PyTorch models faster and simpler.
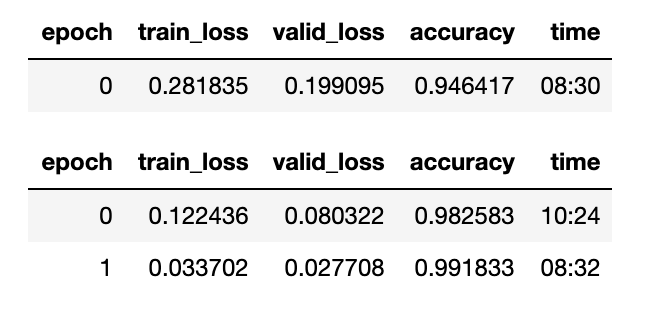
fast.ai training logs - You will learn to use both of these libraries and briefly learn the distinct features offered by each of them.
Who is this book for ?
This book is for data scientists, machine learning researchers, and deep learning practitioners looking to implement advanced deep learning models using PyTorch. Working knowledge of deep learning with Python programming is a plus to get the most out of this book.
Hands-on Python experience as well as a basic knowledge of PyTorch is expected. Because most exercises in this book are in the form of notebooks, a working experience with Jupyter notebooks is expected. Some of the exercises in some of the chapters might require a GPU for faster model training and therefore having an NVIDIA GPU is a plus.
Finally, having registered accounts with cloud computing platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure will be helpful to navigate parts of chapter 10 as well as facilitate distributed training under chapter 11 over several virtual machines.
Buy your copy on Amazon !
You can find the book in kindle format on Amazon . The book is also available on Packt’s own website. If you do read the book, please leave a review based on how you find it. I sincerely hope this book helps you in some way in your deep learning progression trajectory. Happy learning !
Sneak Peek
Here is a glimpse of the book:
Download this pdf here
